Dietary fat can be found in a variety of animal and plant sources. Fatty acids, which form fat molecules, consist of carbon atoms with hydrogen attached, a methyl group, and a carboxyl group. There are different types of fatty acids in our body, with varying structures. There are many types, but today I will focus on saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, which are found in most of the foods we consume on a daily basis. Fat is one of the nutritional macroelements which is essential for our body. It provides physical protection for vital organs in the body, helps to control the body temperature, and is crucial for recovery after exercising. However, not all sources of fat are equally good for us.
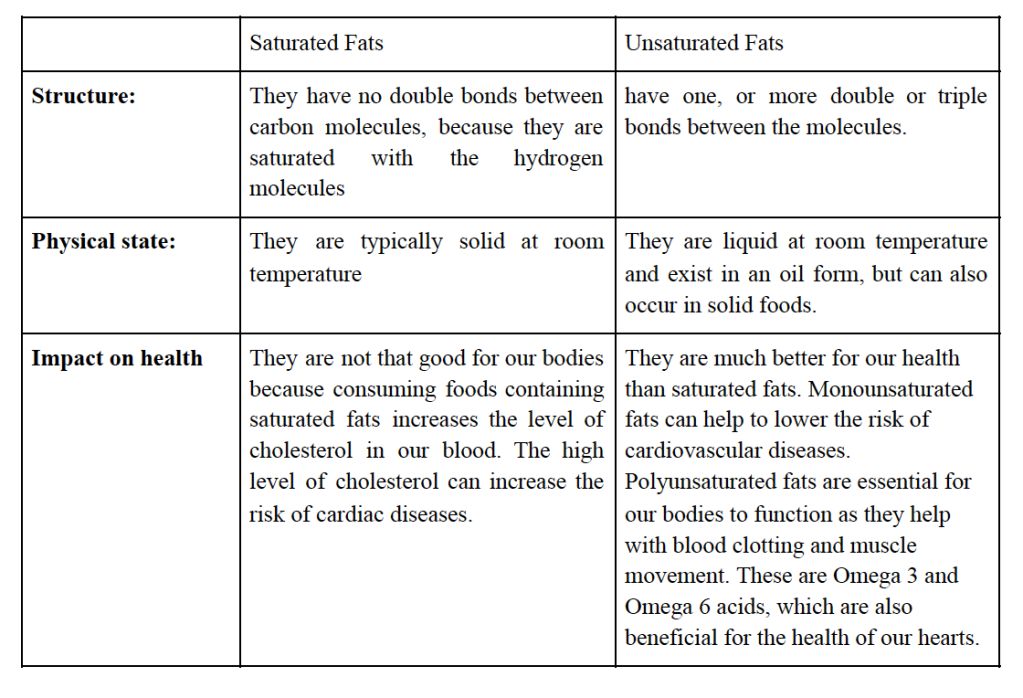
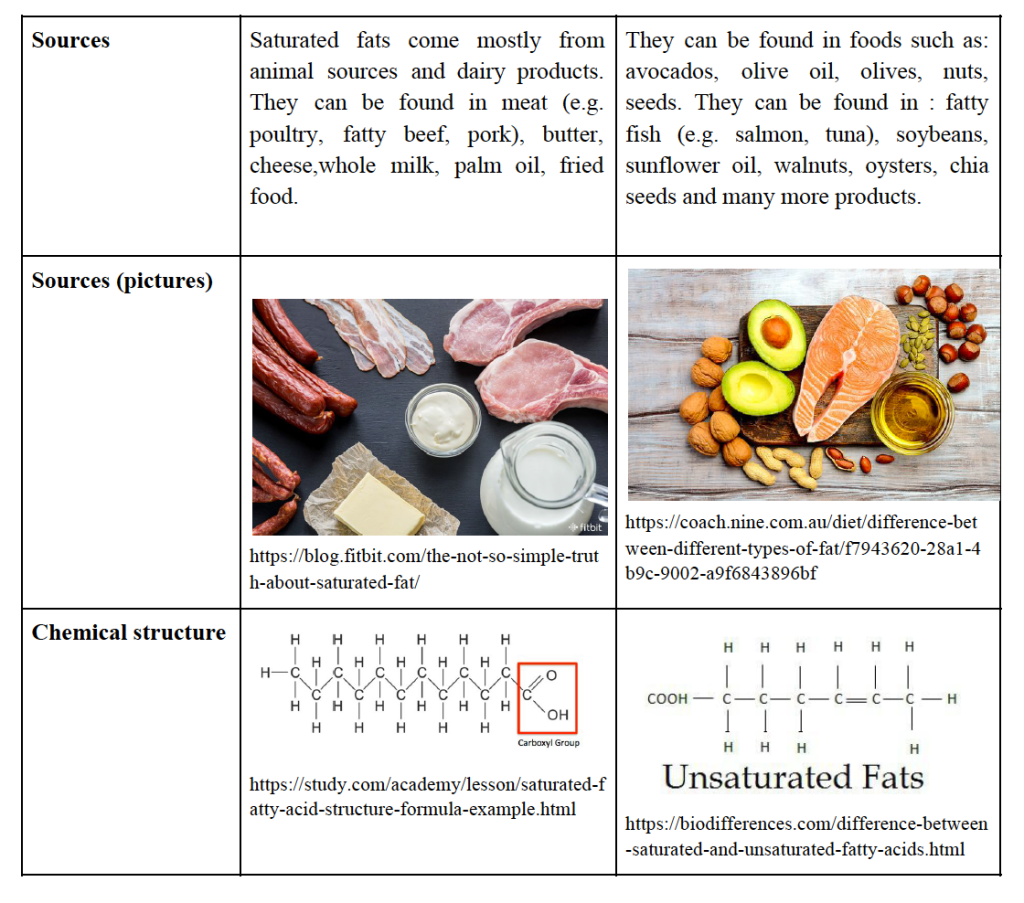
Although healthy fats such as nuts, seeds, plant oils, or fish are key in maintaining a fit and healthy lifestyle, fatty foods such as beef, cheese, or butter increase the level of cholesterol in our bodies and hence contribute to cardiac diseases. This is why it is important to distinguish between healthy unsaturated fats and unhealthy saturated fats, which can cause diseases and obesity. The table below presents the comparison of characteristics typical for saturated and unsaturated fatty acids.
Written by: Zosia Godlewska
Edited by: Anna DeVault
Sources:
SEHS Coursebook for IB Diploma
Is saturated or unsaturated fat better for health? Adam Felman, Medical News Today, January 28, 2020 ; https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/321655
What’s the Difference Between Saturated and Unsaturated Fat? Ann Pietrangelo, Healthline, December 11, 2019 ; https://www.healthline.com/health/food-nutrition/saturated-vs-unsaturated-fat
https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/healthy-eating/eat-smart/fats/saturated-fats